Table of Contents
Trying to figure out what you're actually putting into your body? It feels like everything has a label these days, and sometimes they just raise more questions than answers. Especially when it comes to something as common as milk. You hear about whole milk, skim milk, and then there's low fat. What's the real deal with the middle ground?
Breaking Down 1 Cup Low Fat Milk Nutrition Facts

Breaking Down 1 Cup Low Fat Milk Nutrition Facts
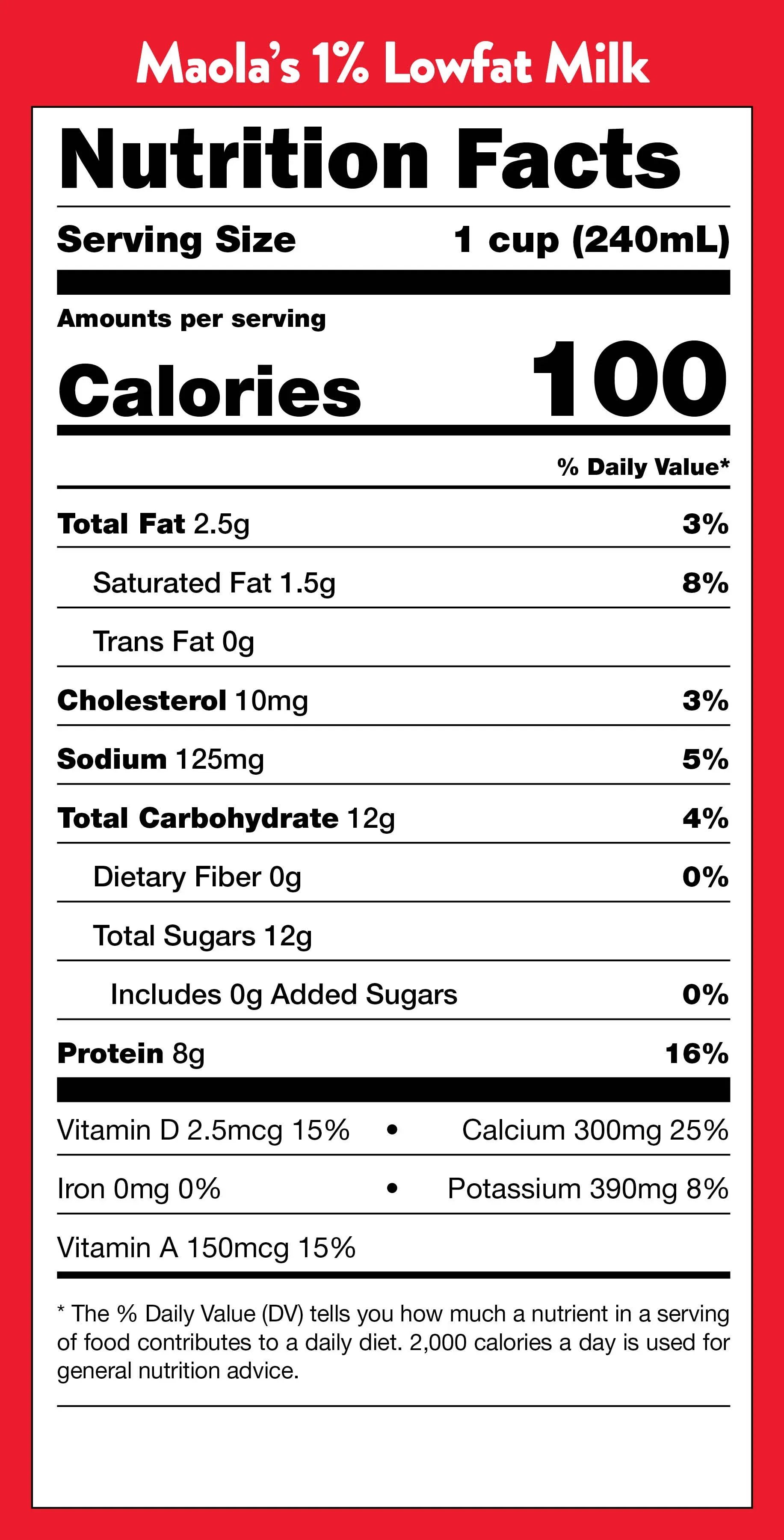
so you're diving into the nitty-gritty of dairy, specificallyBreaking Down 1 Cup Low Fat Milk Nutrition Facts. Forget the fluffy clouds and happy cows for a second. We're talking about what's *actually* in that glass. For a standard cup of 2% low fat milk, you're looking at roughly 122 calories. It's got about 4.6 grams of total fat, which is where the "low fat" part comes in compared to whole milk. Then there are the carbohydrates, sitting around 12 grams, mostly from natural sugars (lactose). And importantly, it packs a solid 8 grams of protein. Think of it as a decent little package of energy and building blocks, not just white liquid.
Beyond the Basics: Vitamins and Minerals in Low Fat Milk
Beyond the Basics: Vitamins and Minerals in Low Fat Milk
The Sunshine Vitamin and Vision Support
so we've covered the big numbers – calories, fat, protein. But low fat milk isn't just about the macros. It's a surprising little powerhouse for things you might not think about daily, like certain vitamins. Take Vitamin D, often called the "sunshine vitamin." It's added to most milk in the US because, frankly, most of us don't get enough sun exposure, and it's tough to find in many foods naturally. This stuff is crucial for your body to actually absorb the calcium we'll talk about next. Without enough D, that calcium just doesn't do its job properly. Then there's Vitamin A, which is important for things like good vision, especially in low light, and keeping your immune system running smoothly. When fat is removed from milk, some of the naturally occurring fat-soluble vitamins like A and D are lost, so they get added back in, which is why you'll see "fortified" on the carton.
Building Bones and Powering Energy
Now, let's talk minerals. This is where milk really shines, and probably what most people think of first. Calcium is the big one, right? You probably heard about it your whole life for strong bones and teeth. And it's true. Milk is a readily available source. But it's not just about bones; calcium is also involved in muscle function and nerve signals. Hand-in-hand with calcium is Phosphorus. These two work together like a tag team for bone health. Phosphorus is also vital for energy production in your cells. It’s not as famous as calcium, but just as necessary. Getting enough of both is key, and milk provides a good ratio.
Nutrient | Amount in 1 Cup Low Fat Milk (approx) | Why it Matters |
|---|---|---|
Vitamin D | 2.9 mcg (120 IU) | Calcium absorption, bone health |
Vitamin A | 149 mcg RAE (500 IU) | Vision, immune function |
Calcium | 305 mg | Bone health, muscle & nerve function |
Phosphorus | 232 mg | Bone health, energy production |
More Than Just Calcium and D
But wait, there's a bit more to the story. Low fat milk also contributes other important nutrients. Riboflavin, or Vitamin B2, is present and helps your body convert food into energy. Vitamin B12 is another one you get, which is critical for nerve function and making DNA. While maybe not in huge amounts compared to some other foods, these smaller contributions add up, especially if milk is a regular part of your diet. Think of low fat milk not just as a drink, but as a multi-vitamin and mineral top-up disguised as something you pour on your cereal or add to your coffee. It's a convenient way to tick off several nutritional boxes at once.
Health Upsides Linked to Low Fat Milk

Health Upsides Linked to Low Fat Milk
Strong Bones Aren't Just for Kids
so we've seen the numbers for1 cup low fat milk nutrition facts, particularly that calcium and Vitamin D. Why does that matter beyond just sounding healthy? Well, think about your skeleton. It's not a static structure; it's constantly being broken down and rebuilt. Calcium is the primary building material, and Vitamin D is the foreman that helps get the calcium where it needs to go. Getting enough of both, especially as you get older, is critical for maintaining bone density. This isn't about guaranteeing you'll never break a bone, but it significantly reduces the risk of osteoporosis, that thinning bone condition that can lead to fractures down the line. It's like investing in your future mobility.
Beyond Bones: Heart and Muscle
But milk's benefits don't stop at your skeletal system. That protein we talked about? Eight grams per cup is a decent amount. Protein is essential for building and repairing muscle tissue. If you're active, or even just trying to maintain muscle mass as you age, protein intake is key. Low fat milk provides a convenient, relatively low-calorie source. There's also some research suggesting a link between dairy consumption, including low-fat options, and a reduced risk of high blood pressure. The combination of calcium, potassium (also found in milk, though maybe not highlighted as much), and magnesium seems to play a role here, helping to regulate blood pressure.
So, are we saying milk is a magic bullet for heart health and bulging biceps? Absolutely not. Diet is complex, and no single food does it all. But including low fat milk can be a straightforward way to contribute positively to these areas as part of a balanced eating pattern. Think of it as one piece of the puzzle.
Consider these potential benefits:
- May support bone density and reduce osteoporosis risk (Calcium, Vitamin D, Phosphorus)
- Contributes to muscle maintenance and repair (Protein)
- Potential link to lower risk of high blood pressure (Calcium, Potassium, Magnesium)
- Provides essential nutrients for overall health (Vitamins A, B12, Riboflavin)
Making it Part of Your Routine
Figuring out how to actually get these nutrients into your day is the next step. A cup of low fat milk is easy. Pour it on cereal, blend it into a smoothie, use it in your coffee or tea, or just drink it straight. It’s a versatile base for getting a dose of protein, calcium, and those added vitamins without a ton of extra fat or calories compared to whole milk. It’s not a requirement for a healthy diet – you can get these nutrients elsewhere – but it's a readily available, often affordable option for many people. Just keep in mind portion sizes and how it fits into your total daily intake.
Choosing and Storing Your Low Fat Milk
Choosing and Storing Your Low Fat Milk
Picking the Right Carton
Alright, so you've seen the1 cup low fat milk nutrition factsand decided to grab some. Standing in front of the dairy case can still be a bit much, right? You've got brands, organic options, lactose-free versions, and different fat percentages. For low fat, you're generally looking for "2% Reduced Fat Milk." That's the standard we've been talking about. Check the expiration date – it's not just a suggestion, it's a safety guideline. Look for cartons that are cold to the touch; if they feel warm, walk away. Also, give the carton a quick check for any damage or leaks. A dented carton might not seem like a big deal, but it could compromise the seal and invite unwanted bacteria.
Keeping it Fresh at Home
Got your milk home? Great. Now, treat it right. Milk is sensitive to temperature changes and light. The fridge door is the worst place for it because the temperature fluctuates every time you open it. Find a spot on an inner shelf, preferably towards the back, where it stays consistently cold. The ideal temperature is below 40°F (4°C). Don't leave it sitting out on the counter while you're making coffee or cereal; pour what you need and get the carton back into the fridge immediately. Simple steps, but they make a huge difference in how long your milk stays good and safe to drink.
- Store milk on an inner fridge shelf, not the door.
- Keep fridge temperature below 40°F (4°C).
- Return milk to the fridge immediately after use.
- Keep the carton sealed tightly when not in use.
Recognizing When Milk Goes Bad
Even with careful storage, milk doesn't last forever. The expiration date is your first clue, but trust your senses too. If the milk smells sour or off, don't risk it. Look for changes in texture; curdling or chunkiness is a definite sign it's time to toss it. The color might also change slightly, becoming more yellow. Tasting it is the final, often unpleasant, confirmation, but if the smell or look is wrong, just dump it. Food waste stinks, sure, but a few bucks down the drain is better than a day spent regretting that questionable gulp.
Making Sense of Low Fat Milk
So, we've looked at the numbers for1 cup low fat milk nutrition facts. It's clear that beyond just being a simple beverage, it offers a specific mix of calories, protein, and essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D. Understanding these details moves beyond general health claims and into practical dietary planning. Whether it fits into your daily routine depends on your individual needs and dietary goals, but knowing the facts provides a solid foundation for that decision.
