Table of Contents
Walk down the dairy aisle these days and you're faced with a wall of choices. Among the most confusing? The endless tubs labeled "full fat" or "low fat." For years, we were told to ditch the fat, believing it was the enemy of health and weight loss. But now, the script seems to be flipping, leaving many scratching their heads and asking: when it comes to yogurt, which is really the better choice? The debate around full fat vs low fat yogurt isn't just about calories; it delves into how different types of fat affect our bodies, our hunger levels, and even the sneaky addition of sugar in products marketed as "healthy." This article cuts through the noise to look at the actual nutrition labels, discuss how these yogurts impact satiety – that feeling of fullness that stops you from raiding the pantry an hour later – and explore what the latest science suggests about fat and weight management. We'll also highlight the often-overlooked issue of added sugars, which can turn a seemingly virtuous low-fat option into a sugar bomb. Get ready to make a more informed choice the next time you grab a spoon.
Understanding the Nutrition: Full Fat vs Low Fat Yogurt
Understanding the Nutrition: Full Fat vs Low Fat Yogurt
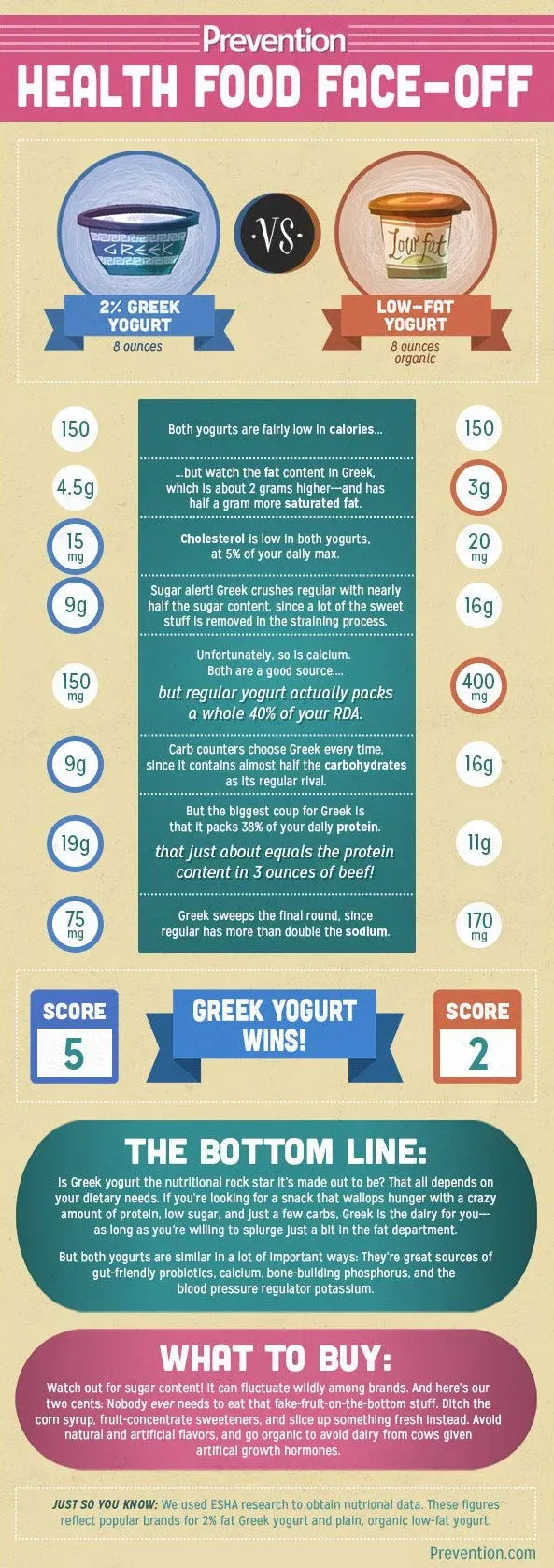
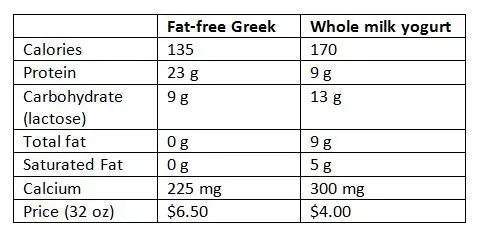
Alright, let's peel back the lid on this yogurt container and actually look at what's inside when we talk about Understanding the Nutrition: Full Fat vs Low Fat Yogurt. The most obvious difference, of course, is the fat content. Full-fat yogurt, made from whole milk, packs more saturated fat than its low-fat or non-fat cousins. This is the core nutritional distinction. Low-fat versions remove some or most of this fat during processing. But here's where it gets interesting – when manufacturers take out the fat, they often need to add something back in to maintain texture and flavor. Sometimes that's thickeners, but more often, it's sugar. So, while the fat grams drop, the sugar grams can climb, which completely changes the nutritional profile you're getting.
So, what are the actual numbers looking like?
Nutrient (Approx. per 100g plain yogurt) | Full Fat | Low Fat |
|---|---|---|
Calories | 60-80 | 40-60 |
Total Fat | 3-5g | 0.5-2g |
Saturated Fat | 2-3g | 0.3-1g |
Protein | 3-4g | 4-5g |
Carbohydrates (Natural Sugars) | 4-5g | 5-6g |
Satiety and Hunger: Does Full Fat Yogurt Keep You Fuller?
The Fat Factor in Feeling Full
let's talk about the real reason many folks are circling back to full-fat dairy: that feeling of actual satisfaction after you eat. When you're weighing full fat vs low fat yogurt, one of the big arguments for the full-fat camp is satiety. Fat, simply put, takes longer for your body to break down and move through your digestive system compared to carbohydrates or protein. Think of it like a slow-release fuel. This slower digestion means food hangs around in your stomach for a bit longer, sending signals to your brain that you've had enough. It’s not some magic trick; it’s just how your body processes different macronutrients.
Signaling the Brain: Hormones and Hunger
Beyond just hanging out in your stomach, fat triggers specific hormonal responses that tell your brain you're satisfied. One key player is Cholecystokinin (CCK), a hormone released in your gut after you eat fat and protein. CCK signals the pancreas to release digestive enzymes and tells your brain to reduce appetite. It's like your gut sending a memo upstairs saying, "Alright, we're good down here, no need to keep looking for snacks." Low-fat or fat-free versions, especially those bulked up with sugar, might give you a quick energy spike, but they often lack the sustained signaling needed to truly curb hunger for a decent amount of time. Ever eat a fat-free, sugary snack and feel hungry again thirty minutes later? Yeah, that's likely why.
Putting Satiety into Practice
So, does this mean full-fat yogurt is a free pass to eat unlimited amounts? Absolutely not. Portion size still matters. However, incorporating a serving of full-fat yogurt into your breakfast or snack might mean you're less likely to experience that mid-morning slump that sends you rummaging for cookies. The increased satiety can help you stick to your eating plan more easily throughout the day. It’s about feeling genuinely satisfied, not just stuffed. When considering Satiety and Hunger: Does Full Fat Yogurt Keep You Fuller?, the evidence points towards yes, largely due to the inherent properties of dietary fat and its impact on digestion and hunger hormones. It's a practical benefit for managing appetite without feeling deprived.
Weight Management and Full Fat vs Low Fat Yogurt

Weight Management and Full Fat vs Low Fat Yogurt
The Satiety Advantage for Managing Weight
let's get down to brass tacks about Weight Management and Full Fat vs Low Fat Yogurt. For years, the conventional wisdom for losing weight was simple: cut the fat, cut the calories. Low-fat everything became the diet mantra. But guess what? People didn't magically get leaner. One reason, as we touched on, is satiety. Full-fat yogurt helps you feel full and stay that way for longer. If a small serving of full-fat yogurt in the morning means you're not famished by 10 AM and raiding the office snack machine, you're likely consuming fewer calories overall throughout the day. It’s not about the calories in that single serving alone; it’s about how that serving influences your eating behavior for hours afterward.
Calories Aren't Everything (Especially with Added Sugar)
Sure, a cup of full-fat yogurt generally has more calories than a cup of plain low-fat yogurt. That much is undeniable. But here's the kicker: that comparison is often apples and oranges. Many low-fat yogurts, especially the flavored ones, are loaded with added sugars to compensate for the lack of flavor and texture when the fat is removed. And those added sugars? They contribute calories, cause blood sugar spikes and crashes that can trigger more hunger, and frankly, are just empty calories your body doesn't need. You might save 20 calories by choosing the low-fat version, but if it's packed with sugar and leaves you hungry sooner, prompting you to eat an extra 200 calories later, where's the win for weight management? It's a classic diet trap.
So, when you're looking at the labels, don't just glance at the fat grams. Look at the total carbohydrates and specifically, the "Includes Added Sugars" line. You might be surprised.
Things to Consider for Weight Management:
- Total calories per serving (including from added sugar).
- How long it keeps you feeling full.
- Whether it fits into your overall daily calorie and macro goals.
- The presence of protein, which also contributes to satiety.
- Your personal preference – sustainability matters more than perfection.
Beyond the Fat: Added Sugar in LowFat Yogurt

Beyond the Fat: Added Sugar in LowFat Yogurt
so we've talked about the fat, but here's where things get really interesting, and frankly, a bit frustrating. When manufacturers strip out the fat from yogurt to make those "low-fat" or "fat-free" versions, they often leave behind a product that's less flavorful and has a thinner, sometimes watery texture. To fix this, they frequently dump in added sugars. It's a classic trick in the food industry: take something out that provides taste and texture (fat), and replace it with something cheap that provides sweetness and masks the blandness (sugar). So, while you might be diligently avoiding fat grams, you could be inadvertently signing up for a significant dose of sugar, which, let's be honest, isn't doing your waistline or your health any favors. This is why focusing solely on whether it's full fat vs low fat yogurt without checking the sugar content is a rookie mistake.
Choosing Your Yogurt: Finding Balance with Full Fat vs Low Fat

Choosing Your Yogurt: Finding Balance with Full Fat vs Low Fat
It's Not a One-Size-Fits-All Deal
Alright, so after wading through the fat grams, calorie counts, and the sneaky sugar situation, you're probably wondering, " just tell me which one to buy already!" If only it were that simple. The truth about Choosing Your Yogurt: Finding Balance with Full Fat vs Low Fat is that the "best" option really depends on you. Your individual dietary needs, your calorie goals, how you plan to eat the yogurt, and crucially, what else is in that specific tub besides milk and cultures. Are you adding it to a smoothie with other calorie sources? Eating it plain as a snack? Using it in a savory dish? All these factors play a role. Blindly grabbing the "low-fat" option because you think it's inherently healthier without flipping the container over to see the sugar situation is, frankly, a mistake many of us made for years. It's time to get a little more savvy than that.
So, how do you start making that call?
- Are you trying to increase your healthy fat intake? Full fat might be better.
- Are you carefully managing saturated fat for specific health reasons? Low fat might be a consideration, but check the sugar!
- Do you struggle with feeling full between meals? The satiety factor of full fat is a plus.
- Are you adding fruit or honey anyway? The natural tang of plain full-fat yogurt handles additions well.
- Is the low-fat option packed with sugar and artificial sweeteners? Probably skip it.
Reading the Label is Your Superpower
Seriously, get friendly with the nutrition label. It's your best tool when navigating the full fat vs low fat yogurt aisle. Don't just look at the fat line. Scan the total carbohydrates and, most importantly, the "Includes Added Sugars" line. A plain full-fat yogurt might have, say, 4-5 grams of natural sugar from the milk. A flavored low-fat version could easily have 15-20 grams of total sugar, with 10+ grams being added sugar. That's a significant difference in terms of how your body processes it and the overall impact on your health and weight management goals. Think about it: a tablespoon of sugar is about 12 grams. You might be eating the equivalent of a spoonful or more of added sugar just by choosing a flavored low-fat option over plain. It's about making an informed choice based on the whole picture, not just the marketing on the front of the container.
Making Your Yogurt Choice
So, after sifting through the details, the answer to the full fat vs low fat yogurt question isn't a simple "always pick this one." Full-fat versions often provide better satiety, which can be helpful for managing hunger, while low-fat options can fit into calorie goals if that's the primary focus. However, the critical factor many miss is the sugar content; low-fat often means more added sugar to compensate for lost flavor and texture. Ultimately, the most sensible approach involves reading the nutrition label carefully, considering your personal dietary needs and goals, and finding a yogurt that offers a good balance of protein and healthy fats without excessive added sugar. Neither option is a magic bullet, but understanding the trade-offs lets you choose the tub that actually supports your health, not just a marketing claim.