Table of Contents
let's talk about low fat chocolate milk. It's that drink that shows up everywhere – school cafeterias, post-workout recovery articles, even your fridge. It tastes pretty good, right? But maybe you've wondered what's *really* in it beyond the obvious milk and chocolate. We're cutting through the marketing hype and digging into the actual low fat chocolate milk nutrition facts.
Low Fat Chocolate Milk Nutrition: Calories, Carbs, Fat, and Protein
Low Fat Chocolate Milk Nutrition: Calories, Carbs, Fat, and Protein
Breaking Down the Calories
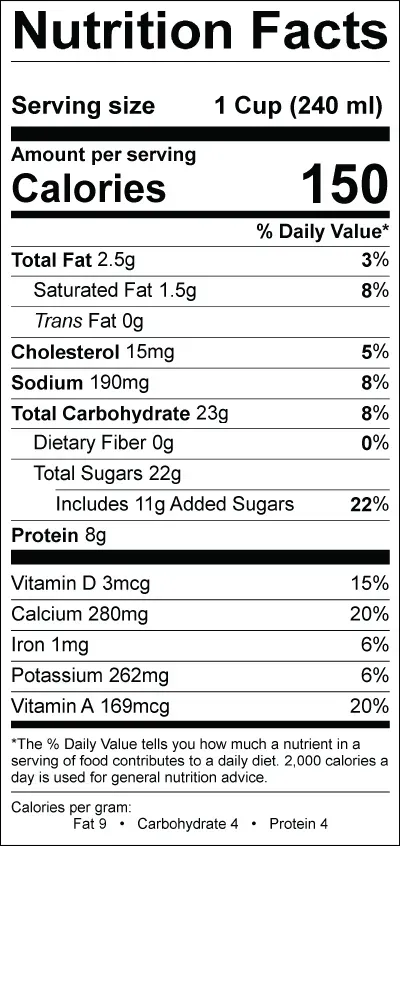
Alright, let's get straight to the numbers. When you pour yourself a standard 1-cup serving of low fat chocolate milk, you're looking at about 158 calories. Now, that's not a huge number, but it's definitely more than plain low fat milk, which clocks in closer to 100-120 calories. Where do those extra calories come from? Mostly the added sugar, which we'll get to in a minute.
Understanding the calorie count is just the first step in grasping low fat chocolate milk nutrition. You also need to see how those calories are distributed. Think of it like a pie chart. A significant slice of this pie comes from carbohydrates, then a decent chunk from protein, and a smaller piece from fat. This breakdown tells you where the energy is coming from.
Fat and Protein: The Building Blocks
Despite the name, "low fat," there's still a bit of fat in there, typically around 2.5 grams per cup. Since it's low-fat milk (often 1%), most of the milk fat has been removed compared to whole milk. This is why it earns the "low fat" label. It’s not zero fat, but it’s significantly less than the 8 grams or so you'd find in whole milk.
On the protein front, low fat chocolate milk delivers about 8 grams per serving. That's the same amount as plain milk. Milk protein, specifically casein and whey, is high quality, meaning it contains all the essential amino acids your body needs. This is one of the more positive aspects of its nutrition profile, especially for muscle repair and growth.
Nutrient | Amount Per 1 Cup | Calorie Contribution (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
Calories | 158 kcal | N/A |
Total Fat | 2.5 g | 23 kcal |
Total Carbohydrates | 26.1 g | 104 kcal |
Protein | 8.1 g | 32 kcal |
Carbohydrates: The Energy Source (and the Sugar)
Now, let's talk carbs. A single cup of low fat chocolate milk packs around 26 grams of total carbohydrates. This is where the energy is, but also where the sugar lives. A big portion of those carbs, about 24.85 grams according to some data, is sugar. Some of that is naturally occurring lactose from the milk, but a significant amount is added sugar to make it taste like, well, chocolate milk.
This high sugar content is the main reason low fat chocolate milk nutrition gets debated. While the carbs provide quick energy, the amount of added sugar is substantial and contributes empty calories without significant nutritional benefits beyond the milk base. It's definitely not a low-sugar beverage, despite being low in fat.
Essential Nutrients in Low Fat Chocolate Milk

Essential Nutrients in Low Fat Chocolate Milk
More Than Just Sugar Water: Essential Nutrients
so we've seen the calorie and sugar situation. It's not exactly a health elixir just based on that. But here's where Essential Nutrients in Low Fat Chocolate Milk come into play and complicate the picture a bit. Beyond the macros, milk is a source of some genuinely good stuff. We're talking about bone-building calcium, which is crucial for, you know, not having your skeleton crumble when you're older. You also get a dose of Vitamin D, often added to milk because it helps your body actually absorb that calcium. Plus, there's potassium, an electrolyte that plays a role in nerve function and muscle contractions. So, while the added sugar is a definite downside, you are getting some nutritional benefits alongside it, which is why it's not quite in the same category as soda.
- Calcium: Good for strong bones and teeth.
- Vitamin D: Helps your body use calcium effectively.
- Potassium: Important for muscle and nerve function.
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): Helps convert food into energy.
- Phosphorus: Works with calcium for bone health.
Fitting Low Fat Chocolate Milk into Your Diet

Fitting Low Fat Chocolate Milk into Your Diet
When Does it Make Sense?
Alright, so we've seen the numbers. It's not perfect, mainly because of the sugar. But that doesn't mean low fat chocolate milk is pure evil. There are specific times when it can actually be a decent choice, especially for athletes or very active people. Think of it as a recovery drink. After a tough workout, your muscles need carbs to refuel their glycogen stores and protein to start repairing. Chocolate milk offers both in a convenient package. The quick carbs help kickstart that recovery process, and the protein gets to work on those tired muscles. It's why you often see it pushed after sports.
For someone who just walked to the mailbox and back, probably not the best daily habit. But if you've just crushed an hour-long run or lifted heavy weights, a cup might be a reasonable option to consider for Fitting Low Fat Chocolate Milk into Your Diet as a recovery tool.
Balancing the Sugar Hit
even if you're using it for recovery, that sugar content is still there. So, if you're going to include low fat chocolate milk, you need to be smart about it. Don't just chug a giant carton without thinking. Portion control is key – stick to that 1-cup serving size. Also, consider what else you're eating that day. If you've already had a lot of added sugar from other sources, maybe skip the chocolate milk or choose plain milk instead. It's about looking at your diet as a whole, not just one drink.
Think of it this way: are the benefits (protein, calcium, recovery carbs) worth the cost (added sugar)? For an athlete needing quick fuel, maybe. For someone sedentary looking for a treat, probably not the most nutrient-dense option. You have to weigh the pros and cons based on your own activity level and overall eating pattern.
- Stick to the recommended 1-cup serving.
- Use it strategically, like after intense exercise.
- Balance the sugar intake with other lower-sugar foods throughout the day.
- Consider if the benefits outweigh the sugar for your lifestyle.
- Don't make it your go-to daily beverage if you're not highly active.
Considering Alternatives
Look, low fat chocolate milk isn't the *only* way to get recovery fuel or essential nutrients. If the sugar is a dealbreaker for you, or you're trying to cut back, there are plenty of other options. Plain low fat milk still gives you the protein, calcium, and Vitamin D without the added sugar. You could add a little unsweetened cocoa powder and a low-calorie sweetener yourself if you crave the chocolate flavor. Or pair plain milk with a piece of fruit for carbs. A protein shake with water or unsweetened almond milk is another common recovery drink, often with less sugar depending on the brand.
Ultimately, the best approach to Fitting Low Fat Chocolate Milk into Your Diet is to be intentional about it. Know why you're drinking it, be mindful of the sugar, and remember you have other options that might align better with your health goals. Is it a mandatory part of a healthy diet? Absolutely not. Can it have a place for some people, at certain times? Possibly, if managed wisely.
As my old coach used to say, "Don't just drink it because it's there. Drink it because it helps you run faster, lift heavier, or recover better."
Understanding the Sugar in Low Fat Chocolate Milk Nutrition

Understanding the Sugar in Low Fat Chocolate Milk Nutrition
The Sweet, Sticky Truth
Alright, let's tackle the elephant in the room when it comes to Understanding the Sugar in Low Fat Chocolate Milk Nutrition: the sugar. We touched on it earlier, but it deserves a closer look. Remember that roughly 24.85 grams of sugar per cup? A chunk of that is lactose, the natural sugar found in milk. That's fine, your body knows how to handle that. The problem is the *added* sugar. That's the stuff manufacturers dump in to make it taste like the chocolate milkshake you dreamed of as a kid. This added sugar contributes calories but none of the vitamins or minerals that make milk valuable. It's essentially empty calories, and consuming too much added sugar is linked to various health issues down the line. So, while the low-fat part sounds good, the high-sugar part is the trade-off you're making for that chocolatey flavor.
Low Fat Chocolate Milk: The Bottom Line on Nutrition
So, we've pulled back the curtain on low fat chocolate milk nutrition. It's not simply "good" or "bad." We've seen the breakdown: around 158 calories per cup, a decent hit of carbs and protein, and yes, a noticeable amount of sugar, sitting around 25 grams. It does bring calcium and vitamin D to the table, which is a plus. The reality is, it's a beverage that provides some nutrients but also contributes significantly to daily sugar intake. Knowing these facts allows you to decide if and how it fits into your overall eating pattern, considering its caloric density and sugar content alongside its protein and micronutrient contributions.
