Table of Contents
Walking down the dairy aisle can feel like navigating a maze. Whole milk, 2%, 1%, skim – what's the actual difference? A common point of confusion boils down to low fat vs nonfat milk. You see them side-by-side, often grab one based on habit or a vague idea of "healthy," but do you really know what you're getting? It's more than just a label; the fat content fundamentally changes the milk's nutritional profile, taste, and even how it behaves when you cook with it.
Low Fat vs Nonfat Milk: The Basic Breakdown
Low Fat vs Nonfat Milk: The Basic Breakdown
What Exactly is Low-Fat Milk?
When you grab a carton labeled "low-fat milk," you're typically looking at 1% milk. Sometimes it's called "lowfat milk" or "1% milkfat." The name tells you the key difference right away: it contains about 1% milkfat by weight. This isn't some arbitrary number; it's a standard set by regulatory bodies. To get to this point, milk goes through a process called centrifugal separation. They spin the milk really fast, which separates the lighter fat from the heavier liquid. They then add back just enough fat to hit that 1% target. It’s a controlled process designed to give you a consistent product every time.
And Nonfat Milk? That's Skim, Right?
Absolutely. Nonfat milk, skim milk, or fat-free milk – they're all the same thing. This is milk where virtually all the fat has been removed during that same centrifugal separation process. We're talking less than 0.5% milkfat by weight, often closer to 0.1%. The goal here is to strip out as much fat as possible, leaving behind the liquid part of the milk with most of its protein, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals still intact. Think of it as the liquid remains after the fat has been shown the door. Understanding this basic difference in processing is the first step in comparing low fat vs nonfat milk.
- Low-fat milk: ~1% fat
- Nonfat milk: <0.5% fat (often ~0.1%)
- Both processed using centrifugal separation
- Nonfat milk is also known as skim or fat-free milk
Nutritional Facts: Comparing Low Fat vs Nonfat Milk
Nutritional Facts: Comparing Low Fat vs Nonfat Milk
so knowing how they strip the fat is one thing, but what does that mean for what’s actually *in* your glass? When you look at the nutritional labels side-by-side for low fat vs nonfat milk, the most obvious difference is, well, the fat and the calories that come with it. Nonfat milk essentially removes almost all the fat, dropping the calorie count significantly compared to 1% milk. However, it’s not just about what's *removed*; the protein and calcium levels remain pretty much the same between the two. This is key – you're not sacrificing those essential nutrients just by going fat-free. Both are typically fortified with Vitamin D, and often Vitamin A, which are fat-soluble vitamins. The difference in fat content slightly impacts how much of these your body *might* absorb, but milk isn't the only source of these vitamins in a balanced diet.
Nutrient (per 1 cup) | Low Fat Milk (1%) | Nonfat Milk (Skim) |
|---|---|---|
Calories | ~100-110 | ~80-90 |
Total Fat | ~2.5g | ~0-0.5g |
Saturated Fat | ~1.5g | ~0-0.3g |
Protein | ~8g | ~8g |
Calcium | ~30% DV | ~30% DV |
Vitamin D | ~25% DV | ~25% DV |
Taste and Texture: Is There a Big Difference Between Low Fat and Nonfat Milk?
Taste and Texture: Is There a Big Difference Between Low Fat and Nonfat Milk?
The Creamy Feel of Low Fat Milk
so we know low fat milk has about 1% fat. That small amount of fat, while significantly less than whole milk, still makes a noticeable difference on your tongue. It gives the milk a slightly richer, smoother mouthfeel compared to its fat-free cousin. It doesn't coat your mouth the way whole milk does, but it avoids the sometimes watery sensation you get from skim. Think of it as a middle ground – you get a touch of that classic milky richness without the higher calorie count. It feels a bit more substantial when you drink it straight or pour it over a bowl of granola.
Nonfat Milk: Lighter, Thinner, and Sometimes Sweeter?
Switching gears to nonfat milk, also known as skim. When you take out most of the fat, you inherently change the physical properties of the liquid. It feels much lighter, almost thinner, when you drink it. The texture is less viscous, less coating. Some people describe it as tasting slightly sweeter than low-fat milk. This isn't because sugar is added; it's often perceived as sweeter because the lack of fat allows the natural lactose sugars to become more prominent on your palate. If you're used to richer milk, skim can feel a bit like drinking flavored water initially, but many people adjust quickly or prefer this lighter profile, especially in coffee or smoothies where other flavors dominate.
- Low Fat (1%):
- Slightly richer mouthfeel
- Smoother texture
- Middle ground between whole and skim
- Nonfat (Skim):
- Lighter, thinner texture
- Can taste slightly sweeter (lactose more prominent)
- Less coating on the palate
Does the Difference Really Matter for You?
Whether the difference in taste and texture between low fat vs nonfat milk matters is entirely subjective. For some, the slight richness of 1% milk is essential for their morning coffee or simply enjoying a cold glass. They find skim too thin. For others, the lighter nature of nonfat milk is exactly what they want, especially if they're mixing it into something or prioritizing the lowest possible calorie count. It really comes down to personal preference and what you're using the milk for. Don't let anyone tell you your preference is wrong; your taste buds are your own final authority here.
Cooking and Baking with Low Fat vs Nonfat Milk
Cooking and Baking with Low Fat vs Nonfat Milk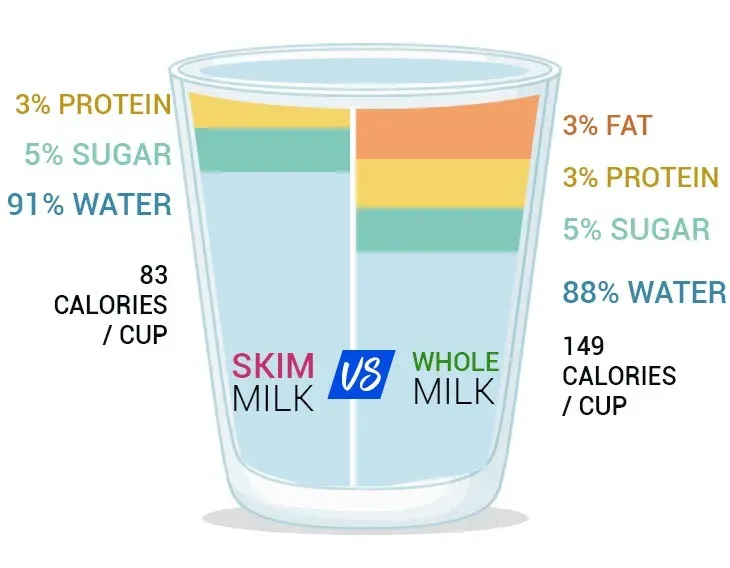
Cooking and Baking with Low Fat vs Nonfat Milk
Alright, let's take this from the glass to the pan or oven. When you're cooking or baking, the fat content in your milk isn't just about calories; it's a functional ingredient. Fat adds richness, provides moisture, and contributes to tenderness in baked goods. Using low fat vs nonfat milk can significantly impact the final result. Nonfat milk, with its lack of fat, can sometimes lead to baked goods that are less tender or sauces that lack that smooth, velvety finish. It can curdle more easily in high-heat situations, like making a cream sauce from scratch. Low-fat milk, with that 1% fat, offers a bit more stability and a touch more richness, making it a slightly more forgiving option in many recipes, though neither will give you the same decadent results as whole milk in something like a classic béchamel or a rich custard. You're trading off some richness for lower fat.
Choosing Your Carton: Deciding Between Low Fat and Nonfat Milk
Choosing Your Carton: Deciding Between Low Fat and Nonfat Milk
Making Your Milk Decision
so you've got the facts: low fat milk has a little more fat and calories, a slightly creamier texture, and offers a touch more flexibility in the kitchen compared to nonfat milk, which is lighter, virtually fat-free, and shines when you want minimal fat impact. Deciding between low fat vs nonfat milk really boils down to what matters most to you. Are you counting every single calorie? Do you crave a richer mouthfeel in your coffee? Are you planning on whipping up a delicate sauce? There isn't a single "right" answer; it's about aligning the milk's properties with your personal health goals, taste preferences, and how you plan to use it. Consider your overall diet and how milk fits in – a glass of 1% might be negligible in calories if the rest of your day is lean, while skim could be the better choice if you're pairing it with a rich meal.
Making Your Milk Choice
So, you've seen the numbers, considered the texture, and thought about how you actually use milk. The low fat vs nonfat milk debate isn't about one being inherently "better" than the other in some grand, moral sense. Nonfat milk strips away most of the fat, leading to fewer calories and a thinner mouthfeel. Low fat milk retains a bit more, offering a slightly richer taste and a few more calories. Your choice really comes down to your priorities: are you counting every calorie, craving a bit more richness, or needing specific performance in your recipes? There's no single right answer, just the one that fits your needs and preferences best.
